
Gonorrhea versus Herpes Simplex Virus
Gonorrhea is a common sexually transmitted disease (STD), and so is herpes.
These and other STDs can be detected through simple blood and lab tests.
Since they can both lead to very serious and in some cases life-threatening situations when left untreated, it makes sense to schedule an appointment with your doctor to see if you suffer from either one of these issues.
According to the World Health Organization, there are 357 million new cases of the four most common sexually transmitted infections (STIs) reported each year, one of them being gonorrhea.
Herpes is even more pervasive.
While 67% of men and women with the herpes virus (either simplex 1 or simplex 2) will never show symptoms or have adverse effects from the infection, they can still transmit the disease.
When symptoms do appear, serious complications can arise if the situation is not treated quickly and properly.
Medical information indicates that as many as 2 in every 3 people between the ages of 15 and 50 currently have some type of herpes infection.
Herpes
There are two different herpes viruses, simplex 1 (HSV-1) and simplex 2 (HSV-2).
Herpes initially appears in or around the genitals or the mouth, which leads to these infections being referred to as genital herpes and oral herpes.
As mentioned above, in most cases, you may have the herpes virus and never show any signs or symptoms.
You may not experience any negative consequences because of the virus.
Human beings have tons of bacterial and viral lifeforms inside them, and in most cases, they do not lead to any adverse health effects.
When herpes does provide symptoms, the most common sign is a red blister or sore.
These blisters can be painful, and they often burst, expelling a pus-like substance.
Herpes is highly contagious when a breakout is experienced, but can be passed to someone else even when no symptoms are present.
Oral-to-genital, genital-to-genital and oral-to-oral contact are the most common ways the herpes virus is passed from one person to another.
However, herpes can be transmitted through incidental contact.
If someone has oral herpes and drinks from a container, and then someone else drinks from that same container, the virus can be passed.
Aside from red blisters or sores, the herpes sufferer may experience an unexpected or abnormal discharge from the penis or vagina, pain during sex or while urinating, and aches and pains around the infected site.
Symptoms may also include fever and headaches, a tingling, burning sensation, fatigue and weariness.
Severe complications include encephalitis, meningitis, partial or total loss of vision, brain-based disorders and other serious health problems.
Additionally, herpes symptoms tend to flareup and to go into remission, rather than stay present over a long period of time.
Gonorrhea
This sexually transmitted disease is not always easy to spot, but it can impact your life negatively whether or not you show symptoms.
Men are generally more likely to show symptoms of gonorrhea than women. However, a woman’s ability to give birth can be severely affected by gonorrhea.
Even in the advanced medical times in which we live, gonorrhea is still responsible for stillbirths and miscarriages, and even infertility among women.
Gonorrhea is passed through oral, anal or vaginal sex, and mothers can pass gonorrhea to a newborn child.
If symptoms appear, they usually do so about 10 to 12 days after infection occurs.
Symptoms in women include painful urination and pain during sex, rectal pain, abnormal discharge of fluids, inflammation in or around the eyes, nausea, lower back pain, sore throat and bleeding between periods.
The most common gonorrhea symptoms for men include frequent and painful urination, pain in the rectum and rectal bleeding, inflamed eyes, and an abnormal discharge from the penis. Less common symptoms include an itching, burning sensation around the head of the penis, a sore throat and pain in the testicles.
Gonorrhea 101
Gonorrhea is a sexually transmitted infection that is caused by bacteria.
It is very common especially in youth between the ages of 15 and 24. It can cause infections in your throat, genitals, and rectal area.
Read on to learn how this disease can be spread, how you can prevent it, symptoms, complications, and how to treat it.
Gonorrhea Transmission
Gonorrhea can be transmitted by having sex with someone who has it. This can be oral, anal, or vaginal sex.
It can also be transmitted from a pregnant woman to her developing baby during childbirth, but not during pregnancy.
Gonorrhea Prevention
If you want to avoid becoming infected with gonorrhea there are a few things you can do.
First, you should know that the only way to totally prevent any STD transmission is to not have sex, including oral, anal and vaginal sex.
However, if you want to remain sexually active you can take steps to reduce your risk of infection.
First, you’re less likely to become infected if you’re in a mutually monogamous relationship with a partner who is not infected.
The only way to know for sure if either of you is infected is to be tested, so it’s a good idea to be tested before beginning any new sexual relationship.
The next step toward preventing gonorrhea transmission is to use condoms correctly and consistently.
That means using the condom every time you have any type of sexual intercourse.
Gonorrhea Symptoms
Gonorrhea can have no symptoms for the majority of people who are infected.
In fact, most women don’t have any symptoms at all or if they do have symptoms they mistake it for some other type of infection.
If you do have symptoms, they may include a burning sensation while urinating, an unusual discharge from the vagina or the penis, and for men painful or swollen testicles and in women vaginal bleeding between periods.
If you have a rectal gonorrhea infection, you may experience an unusual rectal discharge, itching, bleeding, and soreness of the anus as well as painful bowel movements.
If you have any symptoms it’s important to talk with your healthcare provider right away.
But if you find out a partner has been infected, you should talk with your healthcare provider even if you’re symptom free.
Complications from Gonorrhea
If gonorrhea goes untreated, it can cause permanent damage to both men and women.
In women, it can cause pelvic inflammatory disease. This condition can cause permanent infertility and abdominal pain.
In men, the epididymis can become inflamed and become attached to the testicles.
It can also cause sterility.
Infection can also make you more susceptible to becoming infected with HIV.
While rare, if gonorrhea goes untreated for a long period of time it can spread to your joints or bloodstream.
If that happens the condition can be fatal.
Treating Gonorrhea
The good news is that gonorrhea can be easily treated by taking a course of antibiotics.
However, if your infection has gone untreated for a long period of time antibiotics will not be able to undo scar tissue and other damage.
Gonorrhea is a bacterial infection and therefore it is completely curable. One of the biggest myths around gonorrhea is you would know if you had it, but gonorrhea is often asymptomatic which means it has no symptoms.
So, you might not know that you have it.
Gonorrhea tends to be more symptomatic actually in women than in men. So, women might know they have it because they might have a discharge or a burning upon urination.
Men when they have symptoms will also have the same type of symptoms. A discharge or burning upon urination.
And the only way to know that you have it is to get tested.
It is completely curable with antibiotics. A really important fact about gonorrhea is in order to get rid of it both partners need to be treated at the same time and they both need to take their full course of antibiotic in order to rid the body of the infection.
If not, it can keep passing it back and forth or pass it to other partners. Another myth about gonorrhea is that it doesn’t really exist anymore.
And that’s just not true. In certain populations especially young people it’s very much on the rise again. And gonorrhea and chlamydia are often are co-infections.
So, if someone has chlamydia they will often be infected with gonorrhea, as well.
One very important thing to note is that although gonorrhea and chlamydia are completely curable with antibiotics if left undiagnosed and untreated they can lead to infertility in both men and women.
So, it’s really important to follow a medical provider information and follow the prescription that you’re given if you are diagnosed with gonorrhea.
As found on Youtube
Gonorrhea versus Herpes Simplex Virus
Gonorrhea is a common sexually transmitted disease (STD), and so is herpes. These and other STDs can be detected through simple blood and lab tests. Since they can both lead to very serious and in some cases life-threatening situations when left untreated, it makes sense to schedule an appointment with your doctor to see if you suffer from either one of these issues.
According to the World Health Organization, there are 357 million new cases of the four most common sexually transmitted infections (STIs) reported each year, one of them being gonorrhea.
Herpes is even more pervasive. While 67% of men and women with the herpes virus (either simplex 1 or simplex 2) will never show symptoms or have adverse effects from the infection, they can still transmit the disease. When symptoms do appear, serious complications can arise if the situation is not treated quickly and properly.
Medical information indicates that as many as 2 in every 3 people between the ages of 15 and 50 currently have some type of herpes infection.
Herpes
There are two different herpes viruses, simplex 1 (HSV-1) and simplex 2 (HSV-2). Herpes initially appears in or around the genitals or the mouth, which leads to these infections being referred to as genital herpes and oral herpes. As mentioned above, in most cases, you may have the herpes virus and never show any signs or symptoms. You may not experience any negative consequences because of the virus. Human beings have tons of bacterial and viral lifeforms inside them, and in most cases, they do not lead to any adverse health effects.
When herpes does provide symptoms, the most common sign is a red blister or sore. These blisters can be painful, and they often burst, expelling a pus-like substance. Herpes is highly contagious when a breakout is experienced, but can be passed to someone else even when no symptoms are present. Oral-to-genital, genital-to-genital and oral-to-oral contact are the most common ways the herpes virus is passed from one person to another.
However, herpes can be transmitted through incidental contact.
If someone has oral herpes and drinks from a container, and then someone else drinks from that same container, the virus can be passed. Aside from red blisters or sores, the herpes sufferer may experience an unexpected or abnormal discharge from the penis or vagina, pain during sex or while urinating, and aches and pains around the infected site. Symptoms may also include fever and headaches, a tingling, burning sensation, fatigue and weariness. Severe complications include encephalitis, meningitis, partial or total loss of vision, brain-based disorders and other serious health problems.
Additionally, herpes symptoms tend to flareup and to go into remission, rather than stay present over a long period of time.
Gonorrhea
This sexually transmitted disease is not always easy to spot, but it can impact your life negatively whether or not you show symptoms. Men are generally more likely to show symptoms of gonorrhea than women. However, a woman’s ability to give birth can be severely affected by gonorrhea. Even in the advanced medical times in which we live, gonorrhea is still responsible for stillbirths and miscarriages, and even infertility among women.
Gonorrhea is passed through oral, anal or vaginal sex, and mothers can pass gonorrhea to a newborn child. If symptoms appear, they usually do so about 10 to 12 days after infection occurs. Symptoms in women include painful urination and pain during sex, rectal pain, abnormal discharge of fluids, inflammation in or around the eyes, nausea, lower back pain, sore throat and bleeding between periods.
The most common gonorrhea symptoms for men include frequent and painful urination, pain in the rectum and rectal bleeding, inflamed eyes, and an abnormal discharge from the penis. Less common symptoms include an itching, burning sensation around the head of the penis, a sore throat and pain in the testicles.
Transcript:
Of the many sexually transmitted infections, or STIs, gonorrhea is the second most common.
The most common STI is chlamydia.
Chlamydia, and we’ll talk more about chlamydia later. Right now, let’s focus on gonorrhea and why these two happen together.
These two diseases often occur together for two reasons.
First, they have similar risk factors, which include things like having multiple sexual partners and/or having frequent unprotected sex.
The other reason is that infection with one of these bugs makes your body susceptible to a second infection by dampening the immune system.
So I promise we’ll go into more detail about chlamydia later, but for now let’s talk more about gonorrhea.
It’s caused by a bug referred to as neisseria gonorrhoeae, and the reason why we call gonorrhea a sexually transmitted infection is because it undergoes this process referred to as transmission where it moves from one person to another by several mechanisms.
Most commonly, gonorrhea will be transmitted through sex, which can include:
- oral sex
- vaginal sex
- sex.
Another important mechanism of transmission includes childbirth and we’ll talk more about the outcomes of that in a minute, so these are the main ways that gonorrhea can be transmitted.
Let’s move this off to the side and let’s focus instead on my poor friend over here who’s going to have all the different signs and symptoms a person can get with gonorrhea.
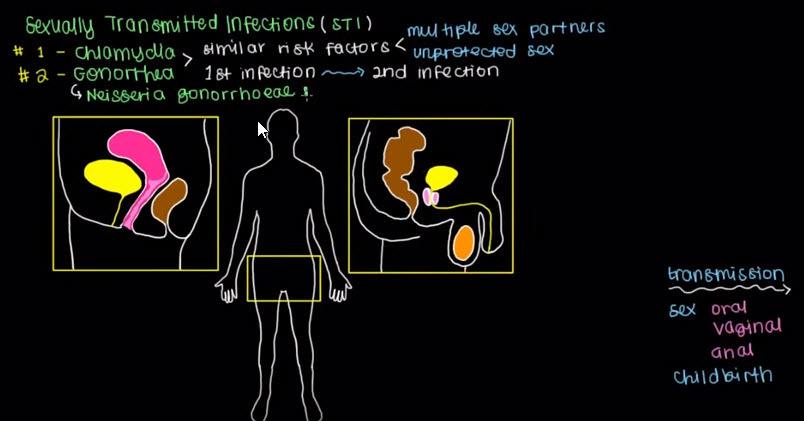
Now because we said the main way gonorrhea spreads from one person to the other is by sex, let’s start by focusing on signs and symptoms at our sexual organs.
So here you can see on the left I have female genitalia drawn out and on the right side, we have male genitalia drawn here.
If we were to imagine our gonorrhea infection, so I’ll use this as sort of a way to mimic gonorrhea as it spreads, perhaps you can have a female infecting a male with gonorrhea and so, because the penis is used during sex, that can actually seed or spread up the urethra.
This yellow line here, that is your urethra. We’ll go into this in more detail in another video but the gonorrhea bacteria will latch on to the walls in your urethra.
Your urethra is lined by epithelial cells, and so this bacterium will enter those cells.
That will trigger an immune response. Your white blood cells will detect that something is wrong and they’ll come up to the urethra through the blood stream to attack wherever the gonorrhea has spread. So if the gonorrhea has only entered a single epithelial cell in your urethra, it’ll cause that cell to die in a process that’s referred to as apoptosis.
Maybe you’ve heard of it. It’s where the body specifically decides to kill a cell because it’s doing something wrong or it’s been infected like in this case.
Now in the ideal world, the white blood cell will kill off this one epithelial cell in the urethra that’s been infected and we’d be done with the infection, but often times there are multiple organisms that kind of spread along the urethral tract, which cause more white blood cells to come from the blood stream to attack the bacteria or the cells that are infected and as a result you get inflammation.
Inflammation of the urethra causing things like pain when you urinate, maybe some burning that’s there as well, and general discomfort.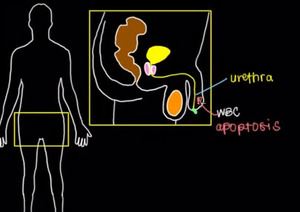
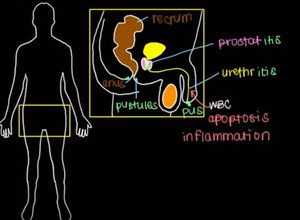
Because of the bacterium, your urethra will cause you a lot of pain and you’ve got what’s referred to as urethritis.
If the gonorrhea spreads up here to your prostate, this pink thing is your prostate, you can get what’s called prostatitis, and this inflammatory process that’s occurring along the way causes white blood cells that may die and epithelial cells that will also go undergo apoptosis with some of the gonorrheal bacteria to sluff off and fall through and come out from the urethral meatus or the end of the penis.
And you can actually see pus coming out of the penis. Now just like the epithelial cells within your urethra, gonorrhea can also effect the epithelial cells that line the anus or even higher up here in the rectum. As a result, you might not see pus coming out from the anus, and instead you might see infections of the cells that line the anus or of the anus.
So this skin infection you’d see here are referred to as pustules.
Pustules. Again, that’s from the gonorrheal bacteria infecting the epithelial cells of the anus. You can also have pustules occur in the female, so let’s label that right here as well as urethritis, but because of the difference in anatomy between the male and the female, you may also see an infection of the vagina, or vaginitis.
More commonly though, infected women will have pain during sex because of pressure that’s put on the cervix due to the gonorrhea that’s spread there causing cervicitis. Cervicitis.
Gonorrhea can spread even further up from the cervix through the uterus and actually come out the fallopian tubes to cause an infection within the pelvic cavity, which is why it’s called pelvic inflammatory disease.
Pelvic inflammatory disease, or PID.
Now from the genital tract, gonorrhea can spread into the blood stream and go elsewhere in the body and quite classically, it goes to your joints like the knee over here to cause arthritis by infecting the joint capsule, so down below here you can see the joint capsule.
Here’s bone, here’s articular cartilage, and this is sonovial fluid or just some fluid in between the two bones in the joint. So if gonorrhea spreads here, think about what else is gonna come right after it. White blood cells. Remember, they’re going to come chasing after the gonorrhea and they’re going to cause inflammation and if you notice in this picture, there’s not a lot of space between the two sets of articular cartilage and the bones here.
If too many white blood cells get into the sonovial cavity, and cause inflammation, you’re going to have a more difficult time using that joint which leads to pain in the knee and difficulty walking. Left untreated, gonorrhea can also spread to the central nervous system. Gonorrhea can infect the lining around the brain and the spinal cord.
This lining is referred to as the meninges; the meninges. An infection of the meninges is referred to as meningitis. Menigitis. Unfortunately, gonorrheal menigitis is more common in children than it is adults. Speaking of children, I mentioned earlier that you can spread gonorrhea through childbirth.
An infected mother can spread the infection if undetected to her child and very early on, you would know if a child is infected with gonorrhea if they look like this.
You’ll notice that the baby may have this very signature crusting of the eyes that’s referred to as gonococcal opthalmia, which is just to say that you have an opthalmic or an eye infection of gonorrhea.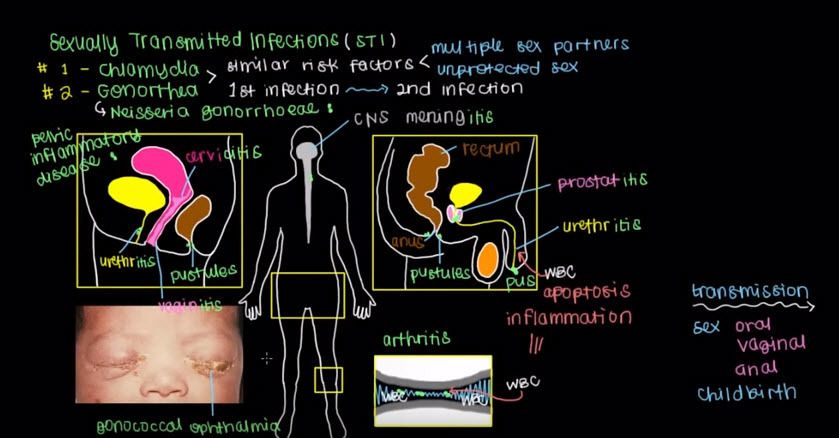
This baby can also have a variety of other issues related to the gonorrhea, such as menigitis, as we talked about or even pneumonia, which is why neisseria gonorrhoeae or gonococcus as one of the bugs pregnant women are often screened for and treated for before they give birth to decrease the odds of this sort of thing happening.
